
Whether it is a small nick or large surgical incision, or a burn, healing is dependent upon the body’s ability to heal itself. A vital role is played by our own natural biomolecules in the healing process, including their contribution to the growth of new cells and the development of new blood vessels that provide nutrients to those cells. Here at Comparative Biosciences, Inc. we are developing the models to test the therapeutics that could accelerate the wound healing process.
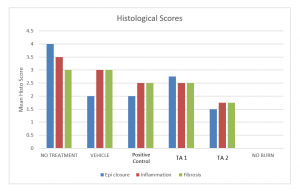
Wound healing studies may be conducted in normal or diabetic (streptozotocin-induced) models. Uniform wounds of full thickness, split thickness or single cuts are created surgically and healing is assessed. The test article is administered and effects of test article on size, rate and character of healing are determined.
CBI offers:
- Surgical wound models
- Dermal burn models
- Full and partial thickness burn- check out our presentation!
- UV light induced
- Chemically and immunologically induced
- Full, split thickness and minced tissue grafts
- Abraded, incisional and excisional
- Hypertrophic scarring models- check out our presentation!
- Ischemic skin
- Rabbit keloid
- Bleomycin and monocrotaline-induced
- Diabetic ulcers
- Pressure wounds
- Corneal laceration and healing
Endpoints for wound healing studies may include:
- Clinical signs
- DRAIZE scoring
- OCT
- Laser Doppler
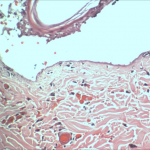
- Histopathology, by our in-house histopathology lab
- Immunohistochemistry
- Histomorphometry/digital image analysis
- Tensile strength
- Transepidermal water loss
- Digital image analysis of wound size and closure
- Body temperature
- Body weights
- Hematology and clinical chemistry
- Serum and tissue markers of inflammation
- Serial biopsies